The end point detection technique is applied to extract the region of interest from the raw speech signal. In other words, it removes the silent region from speech signals. The basic technique of end point detection is to find the energy level of a signal. Signal energy level is calculated in frames, where each frame consists of N samples. The frames are usually overlapped with the adjacent frames to produce a smooth energy line. Fig 1 shows the energy plot of “One”.
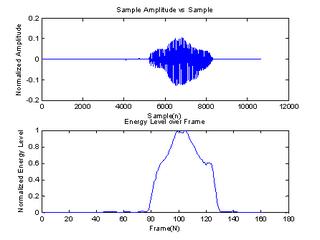
Fig 1: (a) Amplitude vs time plot of “One” (b) energy level of the signal
Accurate end point detection is important to reduce processing load and increase the accuracy of a speech recognition system. Basically there are two famous endpoint detection algorithms. First algorithm uses signal features based on energy levels and second algorithm uses signal features based on the rate of zero crossings. The combination of both gives good result, but nevertheless increases the complexity of the program and also the processing time.
Fig 2 shows the signal of “one” sampled at 8000Hz for 10650 samples or 1.33 seconds. Before the speech begins, the waveform started as silence for about 5000 samples. After the utterance, the signal remains in silence state again for about 2000 samples. Throwing the unwanted silence region, the processing time can be improved to 3650/10650 * 100 = 34.3% by assuming all the frames in the region of interest have been processed. The energy level of the signal is inspected and a threshold value is determined from the energy plot. Fig 3 shows the cropped signal, where the silence region has been eliminated, and the remaining region of interest are used for further processing.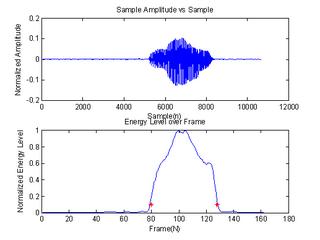
Fig 2: (a) Original signal, (b) End-point detection by using the energy level of the speech signal
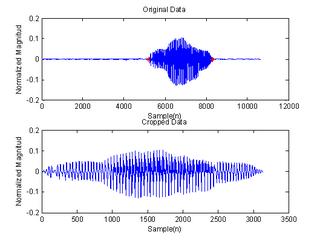
Fig 3: (a) Detected end point, (b) Cropped signal/region of interest

0 comments:
Post a Comment